This study describes the experience of a reference center using continuous aspiration mechanical thrombectomy for acute high- and intermediate-high-risk pulmonary embolism (PE).
MethodsTwenty-nine consecutive patients with acute central PE (48.3% high-risk PE; 82.8% in class >III from the original Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index score; median Charlson Comorbidity Index of 4) were treated with the Indigo® Mechanical Thrombectomy System between March 2018 and March 2020. Technical success was defined as successful placement of the device and initiation of aspiration thrombectomy. Clinical success was defined as any improvement in hemodynamic and/or oxygenation parameters, pulmonary hypertension or right heart strain at 48 hours, and survival to hospital discharge. Safety was defined as freedom from severe adverse events potentially related to the procedure. Three-month follow-up results were collected.
ResultsTechnical success was 96.6%. Miller index and systolic pulmonary arterial pressure were significantly reduced after the procedure (-5.5±3.0, and -10.2±11.5 mmHg, respectively, both p<0.001). There was a significant improvement in mean paO2/FiO2 ratio (+77.1±103.2; p=0.001), shock index (-0.4±0.4; p<0.001), need for aminergic support at 48 h after the procedure (-75.0%, p=0.006) and improvement in right ventricular function in 66.6% (p=0.008). Clinical success was 75.9%. Severe adverse event rate was 10.3%: two deaths during the procedure and one pulmonary macroembolization during device progression. In-hospital and three-month survival rates were 82.8% and 72.4%, respectively.
ConclusionsAspiration thrombectomy for acute high- and intermediate-high-risk PE is feasible with a high technical and clinical success rate. Nevertheless, all-cause mortality is still high, probably related to the baseline high-risk features of the studied population and associated comorbidities.
Este estudo descreve a experiência de um centro de referência no uso de trombectomia mecânica de aspiração contínua na embolia pulmonar (EP) aguda de risco alto e intermédio-alto.
MétodosForam tratados 29 doentes consecutivos com EP aguda central (48,3% alto risco; 82,8% classe >III do score PESI; mediana 4 do índice de comorbilidades de Charlson) com o sistema de trombectomia mecânica Indigo entre março/2018 e março/2020. Definiu-se sucesso técnico como colocação bem-sucedida do dispositivo e início da trombectomia. Definiu-se sucesso clínico como melhoria hemodinâmica, da oxigenação, hipertensão pulmonar e/ou da sobrecarga cardíaca direita às 48 horas; e sobrevivência hospitalar. Definiu-se segurança como ausência de eventos adversos graves relacionados com o procedimento. Registou-se seguimento clínico a três meses.
ResultadosO sucesso técnico foi 96,6%. O índice de Miller e a pressão arterial pulmonar sistólica reduziram-se significativamente (-5,5±3,0 e -10,2±11,5 mmHg, respetivamente, p<0,001). Ocorreu uma melhoria significativa da paO2/FiO2 (+77,1±103,2; p=0,001), índice de choque (-0,4±0,4; p<0,001), necessidade de suporte aminérgico (-75,0%, p=0,006) e melhoria da função ventricular direita em 66,6% (p=0,008). O sucesso clínico foi 75,9%. A taxa de eventos adversos graves foi 10,3%: duas mortes intraprocedimento e uma macroembolização pulmonar durante a progressão do dispositivo. A taxa de sobrevida intra-hospitalar e aos três meses foi 82,8% e 72,4%, respetivamente.
ConclusõesÉ possível proceder a trombectomia de aspiração com níveis elevados de sucesso técnico e clínico. No entanto, a mortalidade por todas as causas permanece elevada, provavelmente relacionada com as características basais de alto risco da população estudada e suas comorbilidades.
Pulmonary embolism (PE) remains a major worldwide health issue. It is the most common cause of cardiovascular death after myocardial infarction and stroke and the leading preventable cause of death in hospitalized patients.1,2
Right ventricular (RV) dysfunction and hemodynamic instability due to acute RV pressure overload are powerful predictors of poor prognosis in acute PE.3,4 Therefore, risk stratification is the first step toward tailoring PE treatment.
For high-risk PE, systemic thrombolysis is usually the appropriate first-line therapy.5–7 However, several population-based studies report underuse of systemic thrombolysis in this clinical scenario.8–10 When there is contraindication due to prohibitive risks of bleeding or failure of systemic thrombolysis, surgical embolectomy or percutaneous catheter-directed therapies (CDTs) are recommended for rapid hemodynamic stabilization.7
For intermediate-risk PE, available data do not support the routine use of systemic thrombolysis.11 However, it should be considered in early signs of hemodynamic decompensation and acceptable bleeding risk.7 In the past decade, several randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses have substantially clarified the optimal management of intermediate-risk PE. In the first instance, these studies focused on the use of full- or low-dose systemic thrombolysis.11,12 Overall, these studies revealed a reduction in early mortality and hemodynamic deterioration, but the benefit was offset by increasing fatal and intracranial bleeding.13 Interest in CDTs has therefore re-emerged as an alternative. These percutaneous approaches include mechanical thrombectomy, catheter delivered thrombolytic therapy (in situ fibrinolysis) and hybrid pharmacomechanical methods.14–16 The goal of CDT is to reduce thrombus burden, pulmonary vascular resistance and, consequently, RV overload.
Despite major advancements in endovascular technology, the role of percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy in the treatment of acute PE remains undefined. To date, no studies have been published on the Portuguese experience with continuous aspiration mechanical thrombectomy for the management of PE.
Therefore, we aimed to present the results of the initial experience of a single reference center assessing the effectiveness and safety of percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy for acute high- and intermediate-high-risk PE.
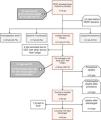
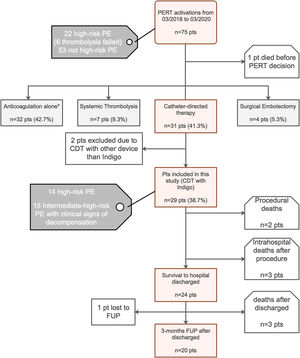
MethodsStudy designOver a 24-month period between March 2018 and March 2020), 75 hospitalized patients with acute PE were screened, 29 of whom were consecutive PE patients undergoing percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy for treatment of proximal location, intermediate-high- or high-risk acute PE, were enrolled (Figure 1: Flow chart). The study was approved by the institutional ethics committee, and the study protocol was written according to the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients before the percutaneous procedure.
Treatment modalities recommended by our institutional Pulmonary embolism response team after its activation and flow chart of the study.
AC: anticoagulation; CDT: catheter-directed mechanical aspiration thrombectomy; FUP: follow-up; PE: pulmonary embolism; PERT: pulmonary embolism response team; pts: patients;
* Reasons for proposing a conservative strategy with isolated AC: PE with >14 days of onset of symptoms – acute on chronic PE (2 pts); intermediate-low-risk PE (1 pt); intermediate-high-risk PE without clinical signs of decompensation with isolated AC (23 pts); active bleeding or contraindication for AC (4 pts) and poor prognosis or cognitive impairment (2 pts).
Patients were referred to thrombectomy if aged 18 years or older. Acute PE was considered as symptoms duration equal to or less than 14 days. A computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) was performed for confirmation of diagnosis, and the presence of intraluminal filling defect in at least one main or lobar pulmonary artery defined the location as proximal.
Prognostic stratification as high- or intermediate-high-risk was performed according to the guidelines published jointly by the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) on the diagnosis and management of acute PE in 2019.7
According to an institutional protocol, based on this ESC/ERS recommendations,7 patients were eligible for thrombectomy if they met one of the following criteria: high-risk PE and absolute or relative contraindication to systemic thrombolysis, high-risk PE and systemic thrombolysis failure (rescue reperfusion therapy) and intermediate high-risk PE with at least one early sign of hemodynamic decompensation. To identify a higher risk cohort of intermediate PE patients, we used a “3+1” rule, previously described, that recognizes patients who may benefit from invasive therapies but do not meet the threshold for systemic thrombolytic therapy17 (see Supplementary Figure 1). Patients were excluded if they presented contraindications for therapeutic anticoagulation (such as active bleeding) or had thrombus in the right cardiac chambers.
Patients were referred for percutaneous procedure from their own institution or other national hospitals. All the referred high-risk and intermediate-high-risk PE cases were discussed by the hospital pulmonary embolism response team (PERT), which is available 24 hours a day, seven days a week; the decision to treat was based on consensus from multidisciplinary PERT.
Study procedureData on patient demographics, medical history, symptoms and physical examination were obtained. Together with results of blood analysis, 12-lead electrocardiogram, transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE), CTPA, anticoagulation therapy, pulmonary angiographic findings, procedural characteristics and invasive hemodynamic measures were collected. In-hospital and three-month outcomes were obtained. All this information was provided by the referring physician and obtained from electronic medical records.
Based on recorded data, validated prognostic stratification scores from the original and simplified Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index (PESI) were computed.18 The Charlson Comorbidity Index score was also calculated for each patient.19
Continuous aspiration mechanical thrombectomyAs a first step, we performed an invasive measurement of pulmonary artery pressures (PAP) followed by an initial pulmonary angiogram to demonstrate the filling defects. Mechanical thrombectomy with an 8-French continuous aspiration mechanical thrombectomy catheter (Indigo CAT8, XTORQ, Penumbra®, Alameda, California) connected to a suction pump (Pump MAX & MAX Canister, Penumbra®, Alameda, California) allowed clot aspiration through negative pressure (20–40 cm H2O) exertion (see Supplementary Table 1 for details of the procedure).
Use of adjunctive in situ thrombolytic therapy (combined method) was according to operator discretion. In these cases, a 5-French pigtail catheter (Cordis®, Miami Lakes, USA) was used for an intravenous drug bolus injection.
At the end of the percutaneous procedure, we performed a final selective pulmonary angiography and reassessed the hemodynamic parameters. Figures 2 and 3 illustrate different situations in which the technique was applied.
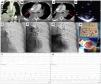
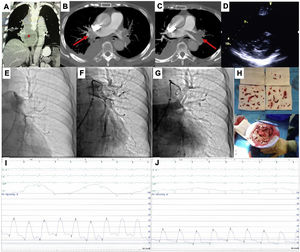
This is the case of a 79-years-old woman admitted with an acute high-risk PE, with contraindication for fibrinolysis due to the presence of a paravertebral mass with medullary compression (A), later diagnosed as a lymphoma (*), underwent endovascular treatment. Axial contrast enhanced computed tomography at time of diagnosis illustrates central extensive bilateral thrombus (red arrows in B and C). Echocardiography at bedside shows an enlarged right ventricle and a flattened interventricular septum in parasternal short axis view (D); Left pulmonary angiography confirm nearly complete obstruction at the origin (E). Aspiration mechanical thrombectomy was performed with the Indigo® CAT8 with improvement of arterial perfusion (F) and venous return (G) of the left lung. Image H displays the extracted clots.
There was a decrease in systolic and mean pulmonary artery pressure of 54 and 33 mmHg pre-procedure (I), respectively, to 34 and 20 mmHg post-procedure (J).
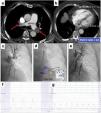
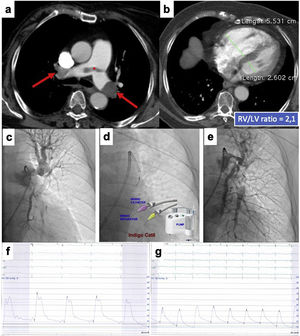
This is the case of an 86-years old woman who had a recent ischemic stroke and was admitted with an acute intermediate-high-risk PE, catheter-directed therapy proposed due to respiratory failure (paO2/FiO2 ratio=170), with no response to parenteral anticoagulation. a) and b) Axial contrast enhanced computed tomography at time of diagnosis illustrates central extensive bilateral thrombus (red arrows) and huge dilatation of right ventricle (RV/LV ratio of 2.1). c) Selective pulmonary angiography confirms obstruction of left inferior lobar artery and lingula. d) Continuous aspiration mechanical thrombectomy was performed with Indigo® CAT8. A Penumbra Indigo System Separator SEP8 device was used through the aspiration catheter to facilitate clot aspiration by preventing the catheter from clogging in the extensive thrombus. e) Post-procedure we observe a near restoration of the normal perfusion in the left lung. f) and g) There was a decrease in systolic and mean pulmonary artery pressure of 65 and 33 mmHg pre-procedure, respectively, to 42 and 25 mmHg post-procedure. PaO2/FiO2 ratio increased to 371 at 48 hours after intervention.
Technical success was defined as successful placement of the devices and initiation of aspiration thrombectomy.20
The Miller Score (MS) was used to quantify thrombus burden through revision of the angiographic findings before and after the procedure and was calculated as previously described21 (see Supplementary Figure 2). The obstruction and perfusion index were assessed by two independent cardiologists. Pre and post-intervention MS and relative MS reduction, defined as the pre-MS minus the post-MS divided by the pre-MS, were calculated for each patient.
Acute procedural success was defined as technical success plus a significant reduction in the vascular obstruction (defined as a relative reduction of at least 10% of MS) and/or reduction of the systolic PAP of at least 10 mmHg at the end of the mechanical thrombectomy, without the occurrence of major adverse events during the procedure.
In-hospital outcomes: Efficacy and safetyClinical success (efficacy outcome) was defined as survival at hospital discharge and one of the following endpoints at 48 hours after the procedure: 1) stabilization of hemodynamic parameters (resolution of hemodynamic shock with no need for vasopressor support); 2) improvement of shock index with reaching values of ratio <1.0; 3) increase in the paO2/FiO2 ratio with reaching values above 200; 4) improvement in pulmonary hypertension, right-sided heart strain or both.
Major adverse event rate (primary safety outcome) was a composite of severe adverse events potentially related to device or procedure and/or severe or life-threatening bleeding in the first 48 hours. Non-major adverse event rate (secondary safety outcome) was a composite of moderate or mild bleeding. Bleeding events were classified by the Global Utilization of Streptokinase and Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Occluded Coronary Arteries (GUSTO) bleeding criteria22 (see Supplementary Table 2).
Short-term outcomes: Three-month follow-upThree months after hospital discharge, short-term outcomes were recorded, including symptomatic recurrence of PE, unplanned right heart failure admission and all-cause mortality. Recurrent PE was defined as symptomatic and objectively confirmed by CTPA, ventilation-perfusion lung scanning or invasive contrast pulmonary angiography.
Within three months after the procedure, patients were clinically reassessed in our Pulmonary Hypertension Clinic. At this time, clinical assessment for persistent dyspnea, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) blood levels were dosed and a TTE was performed for RV function reevaluation and non-invasive pulmonary artery pressure measurement.
Statistical analysisContinuous variables are expressed as mean ± standard deviation or median ± interquartile range (IQR) if distributions are skewed. Categorical variables are summarized as frequency and percentage for each data category. Missing data were not imputed for the efficacy and safety analyses. Comparisons of clinical, laboratorial, echocardiographic and hemodynamic characteristics before and after the procedure were conducted with the two-sided paired Student's t-test or Wilcoxon's non-parametric test (if continuous data), when appropriate, or the two-sided Fisher exact test and McNemar's test (if categorical variables). All reported p values were two-sided and a p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed with Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) software, version 25.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
ResultsBaseline demographicsAmong the 29 patients, mean age was 67.2±14.4 years, and 72.4% were women. Hypertension (72.4%) was the most frequent comorbidity. Common risk factors for PE comprised obesity (body mass index of greater than 30 kg/m2 in 34.8%), immobility within 30 days of PE diagnosis (44.8%) and active cancer (20.7%). History of previous venous thromboembolism was present in 24.1%. The baseline demographics are outlined in Table 1.
Baseline clinical characteristics (n=29).
| Demographics | |
| Age, mean ± SD, years | 67.2±14.4 |
| BMI, mean ± SD, Kg/m2 | 28.1±4.5 |
| Female, n (%) | 21 (72.4) |
| Comorbid conditions and risk factors | |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | 21 (72.4) |
| Current smoking, n (%) | 4 (13.8) |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 15 (51.7) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 5 (17.1) |
| Active cancer, n (%) | 6 (20.7) |
| Immobilization (within previous month), n (%) | 13 (44.8) |
| Auto-immune diseases, n (%) | 5 (17.2) |
| Major surgery or trauma (within previous month), n (%) | 2 (6.9) |
| Estrogen use, n (%) | 3 (10.3) |
| Coronary artery disease, n (%) | 5 (17.2) |
| Prior Myocardial infarction (within previous 3 months), n (%) | 4 (13.8) |
| Congestive heart failure, n (%) | 1 (3.4) |
| History of VTE, n (%) | 7 (24.1) |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index, median (IQR) | 4 (3; 6) |
| Clinical symptoms and signs at presentation | |
| Dyspnea, n (%) | 17 (58.6) |
| Presyncope/Syncope, n (%) | 12 (41.4) |
| Chest pain, n (%) | 3 (10.3) |
| Heart rate, mean ± SD, bpm | 111.3±20.6 |
| Tachycardia>110 bpm, n (%) | 14 (48.3) |
| Shock index>1, n (%) | 18 (62.1) |
| Systolic arterial pressure, mean ± SD, mmHg | 102.1±23.4 |
| Diastolic arterial pressure, mean ± SD, mmHg | 63.0±16.5 |
| Mean arterial pressure, mean ± SD, mmHg | 75.3±17.9 |
| Respiratory rate>20 breaths/min, n (%) | 21 (72.4) |
| Peripheral oxygen saturation, mean ± SD, % | 86.0±18.5 |
| paO2/FiO2, mean ± SD | 212.3±81.0 |
| RV/LV ratio>0.9, n (%) | 29 (100) |
| RV dysfunction, n (%) | 27 (93.1) |
| RV strain on EKG, n (%) | 21 (72.4) |
| Laboratory findings | |
| Lactate level, mean ± SD, mmol/L | 2.6±1.4 |
| Creatinine, mean ± SD, mg/dl | 1.1±0.3 |
| Cardiac T troponin level, median (IQR), ng/L | 76.0 (43.3; 138.8) |
| NT pro-BNP level, median (IQR), pg/Ml | 7898.0 (3152.3; 14340.5) |
| PE risk stratification, n (%) | |
| Original PESI score >III | 24 (82.8) |
| Simplified PESI score ≥1 | 28 (96.6) |
| Intermediate high-risk | 15 (51.7) |
| High-risk with contraindication for lysis | 10 (34.5) |
| High-risk with failed systemic lysis | 4 (13.8) |
BMI: body mass index; BNP: brain natriuretic peptide; IQR: interquartile range; PE: pulmonary embolism; PESI: Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index; SD: standard deviation
Normal reference range: Partial pressure of oxygen >80 mmHg; PO2/fiO2 ratio >400 mmHg; Lactate level <1.2 mmol/L; Cardiac T troponin level <13 ng/L; NT pro-BNP level <88 mmHg (male <50 years), <227 mmHg (male 50-65 years), <153 mmHg (woman < 50 years), <334 (woman 50-65 years)
Original PESI risk strata:18 Class I: Very low 30-day mortality risk (0-1.6%); Class II: Low 30-day mortality risk (1.7-3.5%); Class III: Moderate 30-day mortality risk (3.2-7.1%); Class IV:High 30-day mortality risk (4.0-11.4%); Class V: Very high 30-day mortality risk (10.0-24.5%)
Simplified PESI risk strata: 0 points: 30-day mortality risk 1.0%; ≥1 point(s): 30-day mortality risk 10.9%
Dyspnea was the main presenting symptom (58.6%). Average mean blood pressure, HR and peripheral oxygen saturation values were, respectively, 75.3±17.9 mmHg, 111.3±20.6 bpm and 86.0±18.5%. In 96.6% of patients, CTPA showed bilateral arterial pulmonary involvement. Regarding laboratory findings, mean lactate blood level was 2.6±1.4 mmol/L, median levels of high-sensitivity cardiac T troponin was 76.0 ng/L and NT-proBNP was 7898.0 pg/ml. The electrocardiogram showed repolarization changes consistent with RV overload in 72.4%, complete right bundle branch block in 31.0% and the typical pattern S1Q3T3 in 34.5%. The initial TTE revealed the presence of RV dilation (RV/LV ratio >0.9) in all patients and RV dysfunction in 79.3%. The mean systolic PAP was 61.8±17.3 mmHg and the mean tricuspid annular plane excursion (TAPSE) was 14.5±3.7 mm.
Acute intermediate-high-risk PE and high-risk PE were observed in 51.7% and 48.3% of patients, respectively. In the subgroup of patients with high-risk PE, 71.4% had absolute contraindications for systemic thrombolysis (history of hemorrhagic stroke in two patients, central nervous system neoplasm in two patients and major trauma, surgery or head injury in the previous three weeks in six patients); 28.6% had undergone failed systemic thrombolysis. Thirteen patients were receiving inotropic support before treatment, and three required mechanical ventilation.
More than half of the patients were in class IV or V of the original PESI score (58.6%) presenting a high or very high-risk of 30-day mortality. The median Charlson Comorbidity Index score for the cohort was 4.0 (IQR 3.0-6.0).
Clinical and pulmonary embolism characteristics are presented in Table 1.
Procedural characteristicsProcedural characteristics are summarized in Table 2. Right femoral venous access was the most frequently used (82.8%). Bilateral pulmonary intervention was performed in 72.4% of patients. In situ thrombolytic therapy (bolus injection of alteplase) via catheter was administered to four patients (13.8%) with a median total dose of 10.0 mg (range from 5.0-15.0 mg). This was given at the investigator's discretion because of perceived major thrombus burden and not because of clinical decompensation.
Angiography and procedural characteristics (n=29).
| Angiographic index of severity (Miller score), mean ± SD | 22.0 ± 7.0 |
| Systolic pulmonary artery pressure, mean ± SD, mmHg | 65.0±18.6 |
| Access site, n (%) | |
| Right femoral vein | 24 (82.8%) |
| Left femoral vein | 5 (17.2%) |
| Access closure, n (%) | |
| Perclose proglide system (Abbot Vascular®) | 28 (96.6%) |
| Manual compression | 1 (3.4%) |
| Procedural time, mean ± SD, min | 111.7±46.2 |
| Fluoroscopy time, mean ± SD, min | 40.5±15.8 |
| Contrast volume, mean ± SD, mL | 179.5±92.6 |
| Local of intervention, n (%) | |
| Bilateral | 21 (72.4%) |
| Unilateral, right | 5 (17.2%) |
| Unilateral, left | 3 (10.3%) |
| Thrombolytic infusion catheter, n (%) | 4 (13.8) |
| Total t-PA dose, mean ± SD, mg | 10.0±4.1 |
IQR: interquartile range; PE: pulmonary embolism; SD: standard deviation.
The mean fluoroscopy time was 40.5±15.8 minutes and intra-procedural blood loss was 150-900 ml.
Endpoint analysisThe Indigo CAT8 XTORQ catheter was successfully positioned within the thrombus in 28 patients, achieving 96.6% technical success. In one patient, the catheter was not correctly placed in the right main pulmonary artery owing to catheter kinking at the level of the main pulmonary artery bifurcation due to its marked angulation.
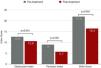
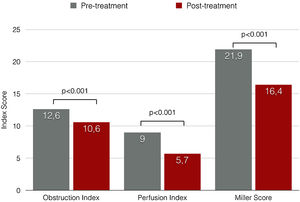
Miller angiographic obstruction index score decreased from 21.9±7.2 at baseline to 16.4±6.5 at procedure completion, revealing a significant reduction in both obstruction and perfusion indexes (p<0.001) (Figure 4). The average of invasively measured systolic PAP decreased from 63.2±19.8 mmHg at baseline to 53.0±17.7 mmHg at procedure completion (mean difference, -10.2 mmHg; p<0.001). Acute procedural success was achieved in 75.9%. A relative reduction of at least 50% of MS was only achieved in 10.3% of the patients.
Considering in-hospital efficacy outcomes, a statistically significant improvement was observed in all of the hemodynamic and oxygenation parameters (Table 3). There was a significant elevation of mean paO2/FiO2 ratio and a significant reduction of shock index. The need for aminergic support significantly reduced from 44.8% to 10.3% of patients in the first 48 hours after the procedure (p=0.006) and RV function improved in 66.6% of the 14 patients who underwent TTE 48 hours after the procedure (p=0.008). Globally, clinical success was 75.9% (10 patients with high-risk and 12 with intermediate high risk PE).
In-hospital efficacy outcomes (n=29).
| Pre-procedure | Post-procedure | Absolute difference | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulmonary artery pressure, mean ± SD, mmHg | ||||
| sPAP | 63.2±19.8 | 53.0±17.7 | -10.2±11.5*1 | <0.001 |
| dPAP | 24.5±9.0 | 21.4±7.9 | -3.1±6.2 | 0.027 |
| mPAP | 37.4±10.8 | 31.6±10.2 | -5.9±7.2 | 0.001 |
| Miller index, mean ± SD | 21.9±7.2 | 16.4±6.5 | -5.5±3.0 | <0.001 |
| PO2/fiO2ratio, mean ± SD | 209.1±84.0 | 286.2± 114.8 | +77.1±103.2 | 0.001 |
| Shock index, mean ± SD | 1.2±0.3 | 0.8±0.2 | -0.4±0.4 | <0.001 |
| Hemodynamic decompensation at 48 hours (hypotension and/or aminergic support), n (%) | 13 (44.8) | 3 (10.3) | -75.0% | 0.006 |
| RV dysfunction, n (%) | 23/29 (79.3) | 4/14 (28.6) | -66.6%*2 | 0.008 |
*1 data not available for 2 patients with major adverse events during procedure;
*2 data available for 14 patients with echocardiogram 48 hours post-procedure.
dPAP: diastolic pulmonary arterial pressure; mPAP: mean pulmonary arterial pressure; PO2/fiO2 ratio: partial pressure arterial oxygen/fraction of inspired oxygen ratio; SD: standard deviation; sPAP: systolic pulmonary arterial pressure.
Concerning primary safety outcomes (Table 4), the major adverse event rate was 10.3%, resulting from the occurrence of two potential procedure-related deaths (as related procedural complications cannot be excluded) and one pulmonary macroembolization during the device progression, followed by cardiorespiratory arrest with need for cardiopulmonary resuscitation, mechanical ventilation and systemic thrombolysis (this patient survived the procedure, but died on day 12 of hospitalization with active urinary cancer). Regarding intra-procedure deaths: One patient died during the procedure due to multiorgan failure in the evolution of cardiogenic shock over several hours; the other patient died at the end of the procedure; PE recurrence was considered the probable cause of death. There were no other treatment-related events, nor any severe nor life-threatening bleeding. Secondary safety outcome occurrence was 17.2%: three patients needed a red cell transfusion within 48 hours without visible bleeding, and two patients had mild hemoptysis during the procedure with no need of percutaneous or surgical intervention or mechanical ventilation.
In-hospital safety outcomes (n=29).
| Major adverse events within 48 hours, a composite of, n (%): | 3 (10.3) |
| - Device or procedure-related death | 2 (6.9) |
| - Pulmonary vascular injury | 0 |
| - Cardiac injury | 0 |
| - Arrhythmias requiring treatment | 0 |
| - Cardiorespiratory arrest with unplanned requirement for ventilation* | 1 (3.4%) |
| - Severe or life-threatening bleeding | 0 |
| Non-major adverse event, a composite of, n (%): | 5 (17.2) |
| - Anemia (without visible bleeding) requiring transfusion but did not result in haemodynamic compromise | 3 (10.3) |
| - Minor bleeding | 2 (6.9%) |
| In-hospital death, n (%) | 5 (17.2) |
Five patients died while hospitalized (in-hospital mortality rate of 17.2%). Three of these deaths are described above, however two additional patients died due to mesenteric ischemia and pneumonia on days 15 and 34 of hospitalization, respectively.
The median length of hospital stay was 12.0 (IQR 16.0) and the median intensive care unit stay was 5.0 days (IQR 6.5).
Short-term outcomes: Three-month follow-upClinical follow-up was completed in 95.8% of patients who survived to hospital discharged (23 patients). Three patients died before completing three months from hospital discharge due to active cancer (Table 5).
Short-term events after hospital discharge.
| All-cause mortality (at 3 months FUP), % (n/N) | 13.0 (3/23) |
| Symptomatic recurrence of PE, % (n/N) | 5.0 (1/20) |
| Pulmonary hypertension, a composite of, % (n/N): | 20 (4/20) |
| - CTEPH | 5 (1/20) |
| - pre-existing CTEPH | 10 (2/20) |
| - pulmonary arterial hypertension (group 1) | 5 (1/20) |
| CTED without rest pulmonary hypertension | 5 (1/20) |
| Unplanned right heart failure admission, % (n/N) | 5.0 (1/20) |
| PE related death, % (n/N) | 0 |
CTEPH: chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension; CTED: chronic thromboembolic disease; FUP: follow-up; PE: pulmonary embolism.
At three months post-procedure, one patient was lost to follow-up and 20 patients were alive. Of these patients, 15 (75.0%) were in World Health Organization functional class I or II. Median value of NT-proBNP was significantly reduced compared to the value before the procedure: median 6833 (IQR 9206) vs 176 (IQR 230); p=0.003. Four patients (20.0%) were diagnosed with pulmonary hypertension confirmed by right heart catheterization, one of them was diagnosed with pulmonary arterial hypertension (group 1) related to an ostium secundum atrial septal defect; the remaining three were diagnosed with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH, group 4). Of these three patients, two had a mean PAP of 50 mmHg before the mechanical thrombectomy and other features of pre-existing pulmonary hypertension. Only one patient (5.0%) developed chronic thromboembolic disease without rest pulmonary hypertension, and another one (5.0%) presented recurrent PE owing to anticoagulation therapy non-compliance. One temporary inferior vena cava filter was implanted after the procedure in one patient with myeloid angiopathy who had a contraindication to long-term anticoagulation therapy.
DiscussionIn our first cohort of patients with acute PE at higher risk, aspiration thrombectomy with Indigo Mechanical Thrombectomy System was feasible for thrombus removal and effective in clinical improvement at 48 hours, displaying acceptable safety in view of the patients’ clinical profile.
According to current guidelines, patients with high-risk PE have a mandatory indication for reperfusion with systemic thrombolysis, due to the high mortality associated with acute RV failure (25%-65%).6,23 However, in ICOPER registry [2], two thirds of patients were ineligible to thrombolysis and in the Registro Informatizado de la Enfermedad Trombo Embólica,24 only 20% of the hemodynamically unstable PE patients received reperfusion treatment. In our series, 10 patients in the high-risk group presented contraindications for thrombolysis. Considering the lack of access to emergent surgical embolectomy in our country, percutaneous thrombectomy using the Indigo® catheter seems to be a promising alternative that broadens the spectrum of patients who can undergo reperfusion in high-risk PE. Additionally, it might be possible to extend the use of aspiration thrombectomy to patients with high-risk PE and high-risk of bleeding (such as elderly and active malignancy). Randomized data to validate this strategy are much needed. Systemic thrombolysis in acute PE is associated with a rate of major bleeding up to 9-24%, including risk of intracranial hemorrhage.13,25 In a prospective registry from De Gregory et al.,26 aspiration thrombectomy in combination with low-dose catheter-directed thrombolysis, as first-line treatment in acute unstable PE, seems to be effective and safe with 2.1% major bleeding.
In intermediate-risk PE, the role of reperfusion is more controversial. In the largest PEITHO trial11 using full-dose systemic fibrinolysis, tenecteplase reduced the risk of death or cardiovascular collapse by 56% in 1006 patients with intermediate-risk PE. However, the benefit was outweighed by a higher risk of severe bleeding and a 10 times greater risk of intracranial bleeding.11 Meta-analyses of systemic fibrinolysis assays in acute PE have shown similar findings.13,27 Concern about the risk of life-threatening hemorrhage, which is close to 3%–5% outside clinical trials,3,28 has reduced enthusiasm for full-dose systemic fibrinolysis and triggered the development of alternative therapies with a lower risk of bleeding, such as aspiration thrombectomy.29,30
Regarding efficacy, in our cohort study, the clinical success 48 hours after aspiration thrombectomy with Indigo® Mechanical Thrombectomy System was numerically superior in intermediate-risk PE (80.0%) compared with high-risk PE (71.4%), similar to other reports of aspiration thrombectomy.31 However, clinical success was slightly lower in our cohort than in the PERFECT registry,32 in which 97.3% of patients had intermediate-risk PE and 85.7% high-risk PE. This difference could be explained for several reasons. Firstly, the selection of patients with intermediate-risk PE for invasive treatment was different in the two studies. It is known that 90-94% of patients in this category of risk will have a favorable evolution with isolated parenteral anticoagulation.11,13 In our cohort, we selected patients with intermediate-risk PE and at least one clinical sign of decompensation, in the attempt to select patients with the highest risk of an unfavorable evolution. It is still unknown which intermediate-risk PE can benefit from an invasive strategy. Further research is needed to clarify the patient-specific risks of decompensation within this category. Secondly, in the PERFECT registry, patients with high-risk PE were treated with mechanical or pharmaco-mechanical thrombectomy, but almost all patients with intermediate-risk PE were treated exclusively with catheter-directed thrombolysis with low-doses of thrombolytics.32 Thereby, the ideal invasive therapeutic strategy, particularly in intermediate-risk PE, remains unclear. Most evidence comes from studies using low dose thrombolysis with ultrasound-facilitated catheter-directed administration (ULTIMA, SEATLE II and OPTALYSE PE trials),33–35 showing improvement in RV function with a good safety profile and reduced rate of major bleeding. Still, data on clinically important outcomes are lacking.30 Most recently, a study using a large-bore mechanical thrombectomy device (FLARE trial)36 also demonstrated good results. Regarding the use of small-bore embolectomy, as Indigo® aspiration system, there are few case series reports in the literature.30,31,37–39 All the published studies found a significant reduction in postprocedural RV/LV ratio with the Indigo® aspiration system in PE.31,37–39 In the Al-Hakim et al. article,37 Indigo® CDT was used to treat six patients with intermediate-risk PE and contraindication for thrombolysis. They reported a significant reduction in systolic PAP (58.2 mmHg vs. 43 mmHg, p<0.05) and Miller index (15.0 vs. 9.8, p<0.01), although similar to our study, complete clearance of thrombi was not achieved. Incomplete removal of thrombi was also observed in up to 80% in the Araszkiewicz et al. study.39 More data on the effectiveness and safety of Indigo® system comes from the recent publication of the prospective trial of the device that included 119 consecutive patients with intermediate-risk PE (EXTRACT-PE trial).40 The authors found a significant reduction in the RV/LV ratio at 48 hours (mean reduction of 27.3%); the low major adverse event rate was 1.7%. In our study, we found an average reduction of 16.1% in mean systolic PAP from pre-procedure to post-procedure, achieved in 86.2% of patients receiving no procedural tPA. These immediate hemodynamic results are quite good compared with data from the EXTRACT-PE trial (8.7% reduction in mean systolic PAP).40
In our cohort, acute procedural success (75.9%), which in its definition, only required partial removal of the thrombus with a relative reduction of at least 10% of MS and/or reduction of systolic PAP at least 10 mmHg, was equal to clinical success (75.9%). It suggests that even small improvements in pulmonary reperfusion can reduce RV strain and increase cardiac output leading to a rapid and effective hemodynamic and respiratory improvement.41 In our series, analyzing only patients who survived at discharge, clinical success of the procedure was 91.7%, revealing the capacity of Indigo® system to cause rapid and significant clinical improvement at 48 hours post-procedure.
Concerning safety, in our cohort, there was no severe or life-threatening bleeds according to GUSTO criteria. In-hospital mortality resembled the results of other cohorts (17.2% versus 22.2% in Ciampi-Dopazo et al. and 16.7% in Pieraccini et al. studies)31,38 explained either by baseline critical condition due to PE severity and by patients’ comorbidities, as assessed by original PESI score (original PESI score >III in 82.8%), rather than to contest the efficacy of mechanical thrombectomy with Indigo® system. The Charlson Comorbidity Index is also a good predictor of in-hospital and long-term outcomes following acute PE.42 In fact, the median Charlson Comorbidity Index of 4 in this cohort indicates that patients were severely ill before the occurrence of pulmonary embolism, explaining the high in-hospital and three-month mortality.
Indigo® Mechanical Thrombectomy System (Penumbra, Inc) enables thrombus removal from the pulmonary circulation, and is highly maneuverable and safe without damaging cardiac and pulmonary structures. The Indigo® catheter has an 8-F outer diameter, which gives it some advantages over devices with a higher profile, such as Flowtriever37 or AngioVAC43,44 such as safety and fast learning curve for handling. Nevertheless, there are some concerns: risk of blood loss during aspiration (10% of patients needed a transfusion at 48 hours in our cohort) and macro and microembolization. We had one case of intraprocedural macroembolization with further hemodynamic instability. After this complication, we started to propose, whenever the patient's stability allows, the study of the peripheral venous system by ultrasound, or preferably, CT angiography to exclude thrombus before the pulmonary thrombectomy.
At three-month follow-up, we observed high mortality, mainly attributable to prexistent severe diseases, as almost all deaths were in patients with active cancer. This does not diminish the clinical value of thrombectomy, although more precise criteria are required for the use of these invasive treatment strategies in patients at an advanced stage of multiorgan failure or with a compromised mid to long-term vital prognosis.
Study limitationsThe present study had several limitations, including a limited sample size from a single center, its observational nature and lack of information about long-term clinical outcomes. In addition, echocardiographic evaluation at 48 hours post-procedure was not performed in all patients due to the retrospective nature of the study and because several cases were referred from other hospitals.
ConclusionsOur data include the first series of patients with acute PE treated with Indigo® Mechanical Thrombectomy nationally. It confirms the feasibility and efficacy of continuous aspiration thrombectomy in the treatment of acute high-risk or intermediate-high-risk with clinical signs of decompensation. There was a significant improvement in clinical parameters such as hemodynamics, gas exchange, and echocardiographic signs of RV overload after aspiration thrombectomy. Nevertheless, all-cause mortality is high, probably related to baseline high-risk features of the study population as assessed by the original PESI and Charlson Comorbidity Index scores.
Before establishing a recommendation for the use of aspiration thrombectomy in acute PE treatment, future prospective randomized studies are needed to confirm and expand our observations and identify patients clearly – especially in the intermediate-high-risk category – who could benefit most from interventional therapies.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
The following are the supplementary material to this article:
Supplementary figure 1 Flow chart of decision-making approach for percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy according to an institutional protocol. AC: anticoagulation; AF: atrial fibrillation; CTPA: computed tomography pulmonary angiography; HR: heart rate; PE: pulmonary embolism; PERT: Pulmonary embolism response team; RV: right ventricular; SBP: systolic blood pressure; ST: systemic thrombolysis; TTE: transthoracic echocardiogram.
Supplementary figure 2 Angiographic Index of Severity (Miller score) which is a form used to grade severity of embolism as judged by the angiographic findings before and after intervention (adapted from reference 21). The obstruction index was calculated based on the following formula: seven major branches were identified in the left pulmonary artery (two in the upper lobe, two in the lingual, and three in the lower lobe), and nine major segmental branches were identified in the right pulmonary artery (three in the upper lobe, two in the middle lobe, and four in the lower lobe). The presence of filling defects (emboli) in any of these branches was scored as 1 point per each segment involved, thus leading to an overall obstruction score ranging from 0 (best) to 16 (worst). The perfusion index, which refers to the effect of embolism on pulmonary artery flow, was scored as follows: each lung was divided into three zones (upper, middle and lower) and the flow in each zone was assessed as absent (3 points), severely reduced (2 points), mildly reduced (1 point), or normal (0 points), thus leading to an overall perfusion score ranging from 0 (best) to 18 (worst). The MS was computed as the sum of obstruction and perfusion indexes in each patient, ranging from 0 (best) to 34 (worst).