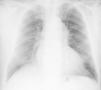
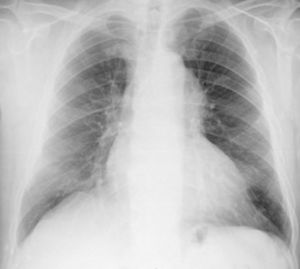
A 63-year-old man presented to the hospital with gradual-onset hoarseness of three months’ duration. He had a history of smoking assessed at 58 pack-years, and no other symptoms such as cough, dyspnea or weight loss. His heart rate was 60 beats/min and blood pressure was 159/67 mmHg; the cardiac exam revealed a diastolic murmur in the aortic area. Indirect laryngoscopy revealed a paralyzed left vocal cord in paramedian position. The chest X-ray (Figure 1) showed a slight mediastinal bulge adjacent to the aortic knuckle but no pulmonary mass.
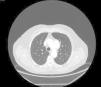
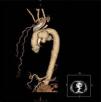
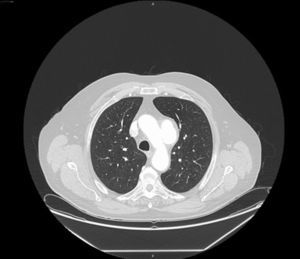
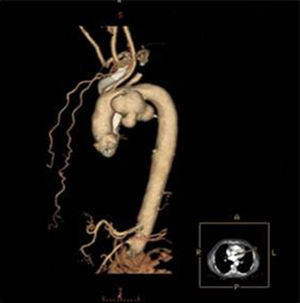
Contrast-enhanced thoracic computed tomography with frontal and sagittal reconstruction (Figures 2 and 3) was performed and revealed a saccular aneurysm of the aortic arch with dilatation up to 6.9 cm and partial thrombosis of the wall.
There was no tumor along the intrathoracic route of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN). The transthoracic echocardiography was normal.
The patient underwent aneurysmectomy and his postoperative course was excellent and uncomplicated, but 12 months after surgery he has not yet recovered from RLN palsy.
Thoracic saccular aortic aneurysm is an important consideration in the differential diagnosis of RLN palsy.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.