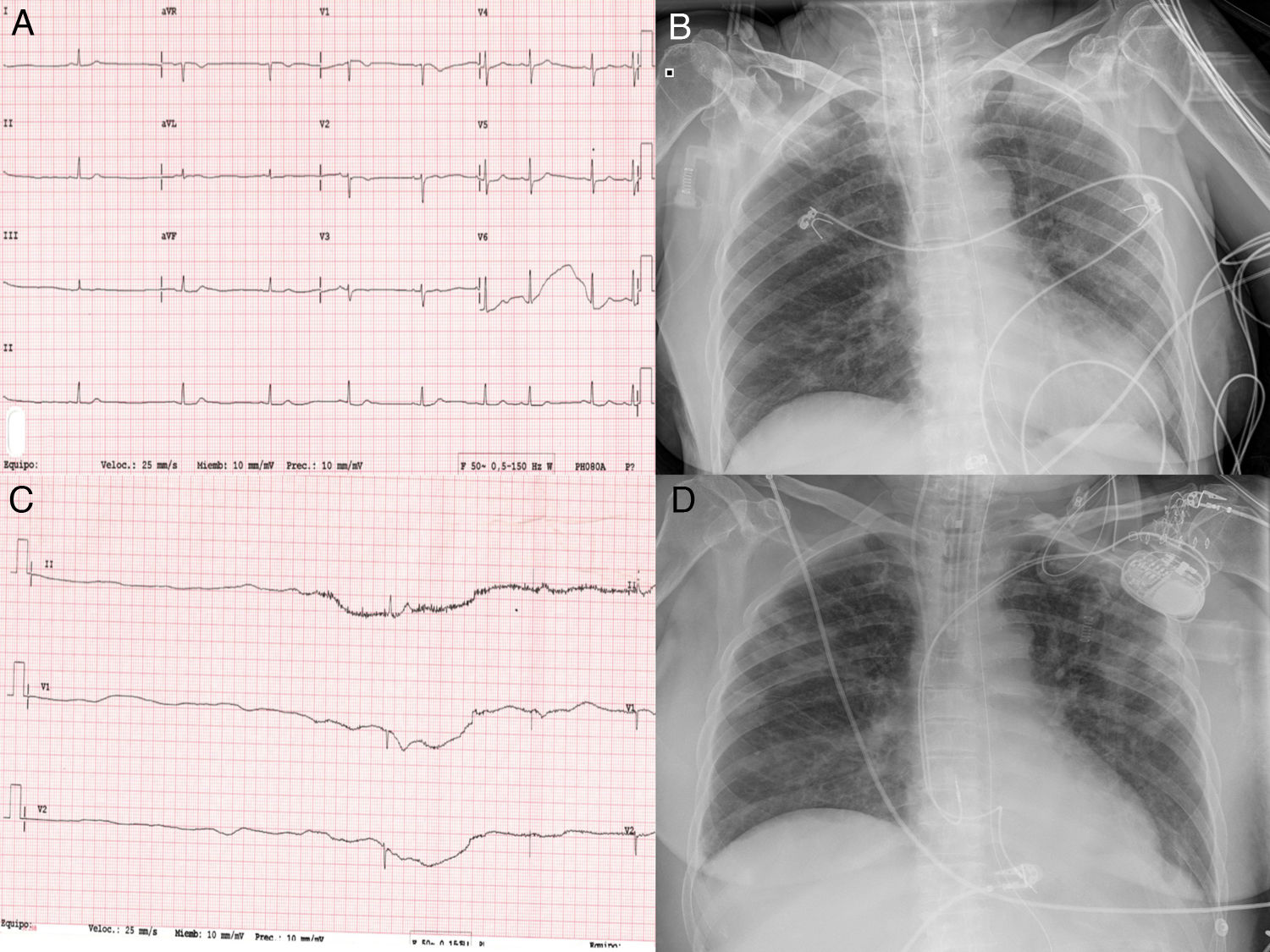
A 75 year-old woman with no previous remarkable clinical history was admitted to hospital with diagnosed COVID-19 diffuse bilateral pneumonia. She was treated with hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir-ritonavir, azithromycin, and methylprednisolone. On day 10 of the hospital stay, she was intubated due to severe hypoxemia. She showed a significant increase of interleukin-6 (105 pg/ml) with normal N-terminal pro-B-type peptide and high sensitive Troponin 1. Interferon beta1-b and tocilizumab were prescribed. On day 33 of the hospital stay, the patient suddenly presented sinus bradycardia and multiple sinus arrest (pauses >10 seconds), Figure 1. An echocardiogram was performed without pathological findings, and a dual chamber pacemaker was implanted without complications. The clinical course was good, and she was discharged from the intensive care unit on day 55 after admission.
Cardiovascular (CV) complications are common in COVID19 patients, including arrhythmias, myocarditis, heart failure and acute coronary syndromes. The systemic inflammatory response to infection could be involved in COVID19-induced CV complications. The possible etiological mechanisms of sinus node dysfunction could be multifactorial, including severe hypoxia, exaggerated response to medication and inflammatory status. Cytokine storm with high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines could directly damage cardiac pacemaker cells contributing to the sinoatrial node dysfunction. To our knowledge this is the first case of sinus node syndrome that required a pacemaker implantation in a critical COVID-19 patient.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.