A 46-year-old male diagnosed with a bicuspid aortic valve and aortic coarctation was admitted for surgical correction of aortic coarctation. He had a personal history of hypertension, renovascular chronic renal failure, and hyperuricemia. The electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm and the echocardiogram revealed preserved ventricular function, a normally functioning bicuspid aortic valve and mild aortic regurgitation.
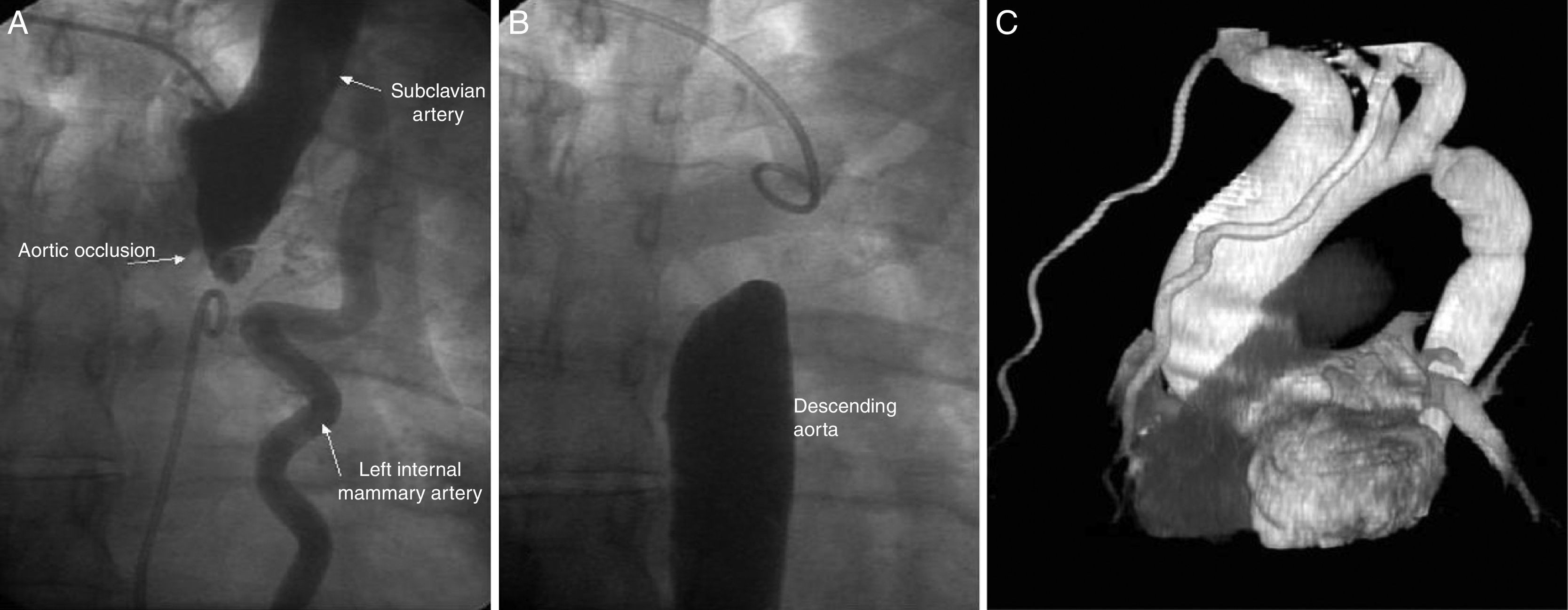
Angiography from the right radial (Figure 1A) and femoral (Figure 1B) arteries showed dilatation of the ascending aorta with maximum diameter of 47mm and aortic coarctation with total occlusion of the descending aorta after the origin of the left subclavian artery (Figure 1A). The gradient between the ascending and descending aorta was 40mmHg. There was an extensive collateral circulation via the intercostal and left internal mammary arteries. Since it was impossible to cross the aortic coarctation, the descending aorta was replaced by a tube graft (Figure 1C).
Aortic coarctation is a narrowing of the descending aorta, typically distal to the origin of the left subclavian artery. It represents 4–6% of all congenital heart defects, with a reported prevalence of 4/10000 live births, and occurs 2–5 times more often in males. It is usually accompanied by other cardiac defects, including bicuspid aortic valve (as in this case), ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, or patent ductus arteriosus.
This patient developed a complete loss of continuity between the ascending and descending aortic segments, resolved by the development of collateral blood flow involving the left internal mammary artery, a mechanism able to maintain long-term hemodynamic stability and absence of symptoms. As a consequence of such collaterals, a significant number of asymptomatic patients are probably not detected until adult life. Aortic coarctation may be relieved by surgery or by transcatheter techniques, but complete aortic coarctation can only be treated by surgery. Without correction, mean life expectancy is 35 years and 90% of untreated patients die before the age of 50 years. Early detection of aortic coarctation is crucial for long-term survival. The importance of this image derives from the small number of cases in the literature of the progression of stenosis into complete aortic coarctation in an adult patient.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.